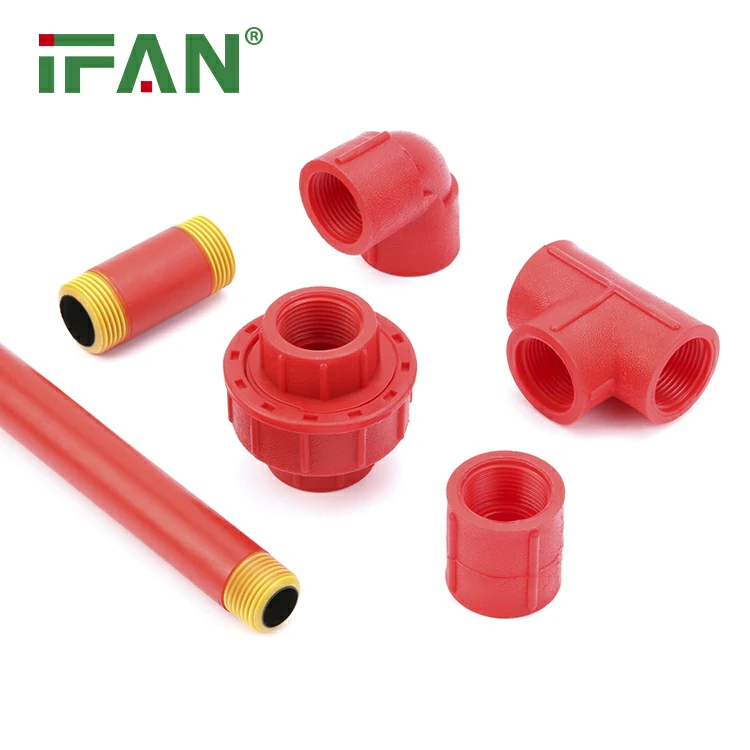
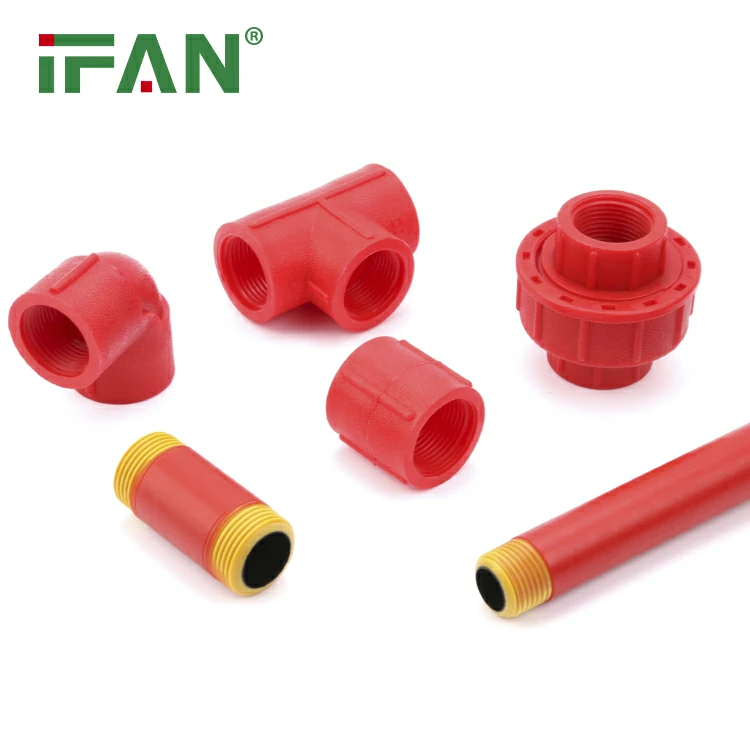
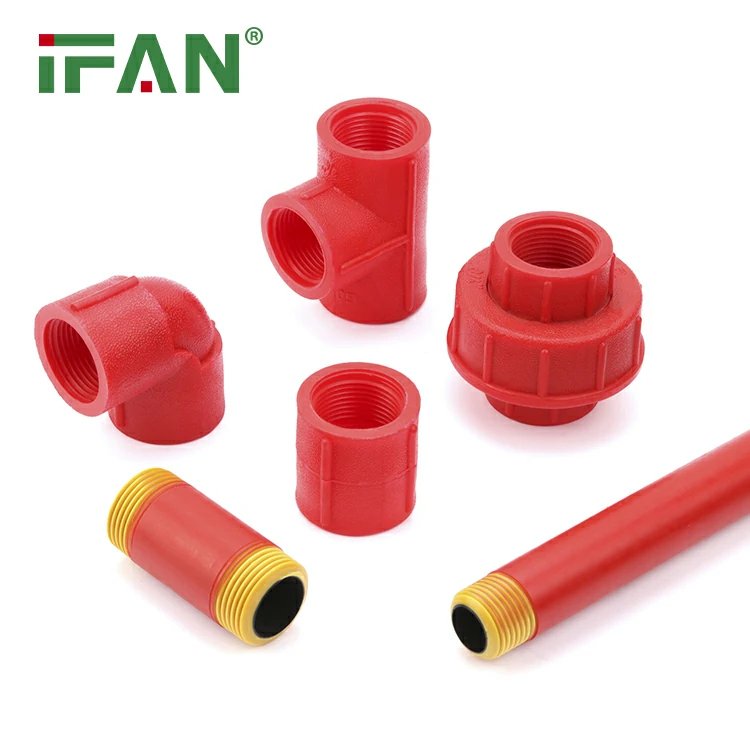
IFAN 1/2″-1″ PPH Pipe Fittings
Category : Click Download
Whatsapp : +86 19884503412
Wechat : 19884503412
Description
Introduction: Understanding PPH Pipe Fittings
PPH pipe fittings are made from polypropylene homopolymer.
They are valued for chemical resistance and mechanical strength.
Commonly used in industrial and chemical piping systems.
Their high-temperature tolerance makes them suitable for various hot fluid applications.
But can they reliably handle domestic or industrial hot water systems?
This article answers that question clearly and thoroughly.
Material Properties and Heat Resistance
PPH material has excellent thermal properties for non-metallic piping.
It typically handles temperatures up to 95°C (203°F) without losing shape.
This makes PPH pipe fittings suitable for many hot water applications.
However, constant exposure to extreme temperatures may cause degradation.
Use cases should be assessed for both temperature and pressure conditions.
Ensure fittings are certified for hot water where safety is essential.
Applications in Hot Water Systems
PPH pipe fittings are commonly used in heating and process water systems.
They are ideal for laboratories, food processing, and industrial cleaning lines.
In residential settings, they can support solar heating or boiler systems.
Example: a factory uses PPH fittings for 90°C circulating cleaning water.
These fittings maintained integrity over several years with no failure.
Always verify manufacturer ratings before system design and installation.
Limitations to Consider
Despite strong resistance, PPH has limitations under prolonged heat.
Sustained temperatures above 95°C may weaken fitting joints.
Thermal expansion can also affect alignment and sealing surfaces.
PPH pipe fittings are not ideal for steam or superheated water.
They should not replace metal fittings in extreme-temperature environments.
Check fluid composition—certain additives may accelerate thermal aging.
Comparison with Other Materials
Compare PPH pipe fittings with PEX, CPVC, and metal alternatives.
PEX handles similar temperatures but may deform under long exposure.
CPVC tolerates higher temperatures, but it’s more brittle.
Metal pipes resist high heat but may corrode in some systems.
PPH is a good compromise—chemical resistance with decent thermal tolerance.
It’s especially beneficial in corrosive or acidic hot water systems.
Installation Best Practices
Use proper tools and techniques to install PPH pipe fittings.
Socket fusion and butt fusion are common joining methods.
Ensure clean, square pipe cuts and precise temperature control.
Do not install PPH fittings near open flames or heat sources.
Support pipes adequately to manage expansion and contraction.
Use thermal insulation to stabilize temperature and extend lifespan.
Testing and Certification
Reliable PPH pipe fittings are tested under high-temperature, high-pressure conditions.
Look for ISO 15874 and DIN standards on packaging or documentation.
Ensure compliance with local plumbing codes for hot water use.
Pressure testing is essential after installation to confirm performance.
Use data sheets to confirm maximum operating limits before design.
Certified products ensure safety and long-term reliability under heat exposure.
Conclusion: A Smart Choice When Applied Right
PPH pipe fitting can be used for hot water, depending on application specifics.
They offer a balance of thermal performance, durability, and chemical resistance.
For water temperatures under 95°C, they are highly reliable.
Industrial and residential systems both benefit from proper use of PPH.
Always follow best practices and check technical specifications.
With care and correct design, PPH pipe fittings serve hot water systems efficiently.
相关产品
- PPH Fittings
IFAN Plastic PPH Pipe Fittings
- PPH Fittings
IFAN ISO 15494 PPH Nipple
- PPH Fittings
IFAN ISO 15494 PPH Equal Elbow
- PPH Fittings
IFAN PPH End Cap
HAVE ANY QUERIES? SEND TO CONTACTOANTSMACHINE.COM
ONTACT US